
FAQ About Cultural Influence of Phoenician Alphabet on Modern Scripts
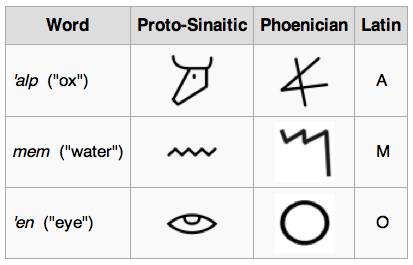
What is the Phoenician alphabet?
The Phoenician alphabet is an ancient script developed by the Phoenician civilization around 1050 BCE. It is considered one of the first alphabets in the world and consists of 22 consonantal letters. This writing system is known for its simplicity compared to earlier scripts like cuneiform and Egyptian hieroglyphs.

How did the Phoenician alphabet influence the Greek alphabet?
The Phoenician alphabet significantly influenced the Greek alphabet. The Greeks adopted the Phoenician script around the 8th century BCE, modifying it to suit their language needs by adding vowels. This adaptation was crucial for the development of Western writing systems.

In what ways did the Phoenician alphabet impact the Latin alphabet?
The Latin alphabet was derived from the Etruscan alphabet, which itself was heavily influenced by the Greek version of the Phoenician alphabet. This chain of adaptation shows the direct influence of the Phoenician script on the alphabet used by much of the Western world today.

What role did the Phoenician alphabet play in the development of the Arabic script?
The Arabic script was indirectly influenced by the Phoenician alphabet through its descendant scripts such as Canaanite and Aramaic. These scripts facilitated the development of the Nabataean script, which is the direct ancestor of the Arabic script.

Why is the Phoenician alphabet important for modern language communication?
The Phoenician alphabet is pivotal in the history of writing because it laid the groundwork for many major alphabets that are still in use today, including Latin and Greek. This influence has enabled the development and expansion of global communication.

What features made the Phoenician alphabet innovative for its time?
The simplicity and efficiency of the Phoenician alphabet were revolutionary, introducing a phonetic system that represented sounds with symbols. This made reading and writing more accessible and adaptable to various languages compared to complex ideographic systems.

Can you see the cultural traces of the Phoenician alphabet in modern alphabets?
Yes, the cultural traces of the Phoenician alphabet are evident in modern scripts through structural similarities and shared symbols. The evolution of individual letters can be traced back to Phoenician origins, especially in the case of Latin and Greek letters.

How did Phoenician merchants contribute to the spread of their alphabet?
The Phoenician merchants were instrumental in spreading the alphabet through trade and colonization. As a seafaring and mercantile civilization, they interacted extensively with neighboring cultures, introducing their writing system across the Mediterranean region.

Did the Phoenician alphabet include vowels?
No, the Phoenician alphabet did not include vowels; it was an abjad, a type of writing system where each symbol primarily represents a consonant. Later scripts, like the Greek alphabet, adapted the Phoenician script by adding vowels.

What is the legacy of the Phoenician alphabet in cultural exchange?
The Phoenician alphabet's legacy in cultural exchange is profound, as it provided a universal means of communication that transcended linguistic barriers. This enabled cultural and economic exchanges across vast distances, laying the foundations for globalization.

How did the Phoenician alphabet help in the development of Western civilization?
The Phoenician alphabet helped forge critical cultural ties in the ancient world, facilitating the spread of ideas and innovations throughout Western civilizations. Its influence on Greek and Latin scripts contributed to the foundations of Western literacy and education.

What materials did the Phoenicians use for writing?
The Phoenicians primarily used papyrus, pottery, stone, and metal for writing. This variety of materials helped ensure the preservation and dissemination of their script across different regions and cultures.

How does the Phoenician alphabet compare to cuneiform writing?
The Phoenician alphabet offered a marked improvement over cuneiform writing by simplifying the system of symbols. Instead of hundreds of signs, it relied on 22 characters, making it far easier to learn and tailor to different languages.

What are the modern countries where the Phoenician alphabet was originally used?
The Phoenician alphabet was primarily used along the coastal regions of the Mediterranean, in what are now modern-day Lebanon, Syria, and parts of Israel and Palestine. Its use spread with Phoenician trade and colonization efforts.

When was the Phoenician alphabet first developed?
The earliest known inscriptions in the Phoenician script date back to around 1050 BCE. It quickly spread throughout the Mediterranean as a dominant writing system due to its efficiency and adaptability.

How did the adaptation of the Phoenician alphabet lead to diversity in modern scripts?
The adaptation of the Phoenician alphabet by various peoples led to the creation of different scripts tailored to unique language needs, resulting in the diverse alphabets we see today, including Latin, Greek, Hebrew, and Arabic.

Is the Phoenician alphabet still in use today?
The Phoenician alphabet itself is not in use today, but its legacy continues through the alphabets it influenced, which remain prevalent across the world in various regions and nations.

What is the impact of the Phoenician alphabet on global languages?
The Phoenician alphabet had a massive impact on global languages by serving as the precursor to various alphabets that form the basis of many modern languages. This has enhanced communication and mutual understanding among different cultures over centuries.

How did the simplicity of the Phoenician alphabet aid its transmission across cultures?
The simplicity of the Phoenician alphabet made it highly adaptable and easy to learn, facilitating its spread across diverse cultures and regions. Its straightforward system was more accessible to peoples unfamiliar with complicated scripts like hieroglyphs or cuneiform.

Did the Phoenician alphabet influence writing systems in non-Mediterranean regions?
While the direct influence of the Phoenician alphabet was strongest in the Mediterranean region, its indirect impact can be seen in the evolution of scripts as far as India, through intermediary scripts that evolved from Phoenician roots like Aramaic.
