
FAQ About Indoor Plant Growth Regulators and Hormones
What are plant growth regulators?
Plant growth regulators (PGRs) are chemical substances that significantly influence the growth and differentiation of plant cells, tissues, and organs. They can be natural hormones produced by plants themselves or synthetic compounds that mimic these hormones. PGRs are used to regulate various aspects of plant growth, such as flowering, fruiting, and ripening, and are frequently utilized to improve the overall quality and yield of plants.

How do plant hormones affect indoor plants?
Plant hormones, also known as phytohormones, play crucial roles in regulating physiological processes within plants. For indoor plants, hormones such as auxins, gibberellins, cytokinins, abscisic acid, and ethylene influence growth patterns, flowering, root development, leaf drop, and other essential functions. By managing hormone levels, indoor gardeners can optimize plant health and growth rates, as well as control undesirable traits.

What is the difference between plant hormones and growth regulators?
While all plant hormones are a type of growth regulator, not all growth regulators are plant hormones. Plant hormones are naturally occurring compounds that control growth and development processes, while growth regulators include both these hormones and synthetic substances designed to alter plant growth in particular ways. Essentially, growth regulators encompass a broader category that includes any substance, natural or synthetic, used to modify plant growth.

Can plant growth regulators be harmful to indoor plants?
While plant growth regulators can be beneficial for promoting specific desirable traits, inappropriate usage can cause harm to indoor plants. Overapplication or the use of incorrect PGRs can lead to stunted growth, leaf burn, or undesirable changes in plant development. It's crucial to follow manufacturer instructions carefully and understand the specific needs of your plants when applying PGRs.

How can plant hormones promote flowering in indoor plants?
Certain plant hormones can be used to induce and enhance flowering in indoor plants. Gibberellins and cytokinins are commonly used to stimulate flowering. They help by promoting cell division and elongation, leading to the development of flowers. Using hormone treatments effectively can result in more abundant blooms and can synchronize flowering phases for ornamental purposes.

Are there natural alternatives to synthetic plant growth regulators?
Yes, several natural alternatives to synthetic plant growth regulators exist. These include organic root exudates, seaweed extracts, humic substances, and compost teas, which can enhance plant growth similarly to synthetic PGRs. Many gardeners prefer natural alternatives due to their sustainability and reduced environmental impact. However, the effects can vary widely depending on the type and concentration of the natural product used.

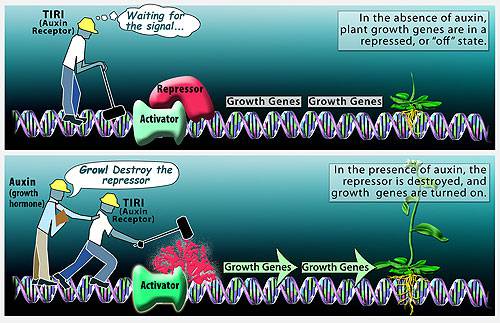
What are auxins, and how do they affect plant growth indoors?
Auxins are a class of plant hormones that play a critical role in the coordination of many growth and behavioral processes in the plant's life cycle. They are primarily responsible for cell elongation, apical dominance, and root initiation. In indoor plants, auxins can be used to promote root growth, enhance stem flexibility, and improve overall plant symmetry and structure.

Can gibberellins be used to improve indoor plant growth?
Gibberellins are a group of plant hormones that are especially effective in promoting plant growth and development. In indoor gardening, gibberellins can be used to elongate stems, increase leaf size, enhance flower development, and improve overall biomass. However, care must be taken to apply the correct amounts, as excessive use can lead to overly rapid growth, weakening plant structure.

What role do cytokinins play in plant growth regulation?
Cytokinins are plant hormones that influence cell division and growth in plant roots and shoots. They are vital for delaying senescence, enhancing nutrient mobilization, and promoting shoot initiation and development. In indoor plants, cytokinins can be applied to stimulate bud growth, prevent leaf aging, and improve greening, making them useful for ornamental plants and enhancing foliage.

How does abscisic acid influence indoor plants?
Abscisic acid (ABA) is a plant hormone that primarily functions to help plants respond to stress conditions, such as drought and cold. It helps regulate stomatal closure, reduces water loss, and stabilizes plant metabolism under stress. For indoor plants, ABA can be crucial in managing water use efficiency and preparing plants for periods of reduced hydration or environmental stress.

What is ethylene's effect on indoor plants?
Ethylene is a gaseous plant hormone that plays a significant role in fruit ripening, flower wilting, leaf abscission, and response to stress. In indoor plants, ethylene can be used to control the ripening process of fruits and the senescence of flowers. However, excessive ethylene exposure can lead to premature leaf drop and other stress-related responses, necessitating careful management.

Are there any side effects of using growth regulators on indoor plants?
Yes, the misuse of growth regulators can lead to several adverse effects on indoor plants. These may include stunted growth, leaf yellowing or scorching, abnormal flower or fruit development, and increased susceptibility to pests and diseases. It's important for users to strictly adhere to recommended dosages and application guidelines to mitigate these risks.

Is it possible to use growth regulators in hydroponic systems?
Absolutely, growth regulators can be effectively used in hydroponic systems. They aid in manipulating growth rates, improving root development, and enhancing nutrient absorption in soilless growing environments. However, the application should be carefully controlled, as nutrient solutions directly affect roots and can lead to rapid changes.

How do natural and synthetic growth regulators differ in their applications?
Synthetic growth regulators are specifically formulated to target precise plant processes and often provide more predictable results compared to natural alternatives. Natural regulators, derived from organic matter, are less concentrated and can vary in effectiveness due to their complex nature. Many growers prefer natural products for their organic context, while synthetics are chosen for precision and reliability.

What precautions should I take when using growth hormones on houseplants?
When using growth hormones on houseplants, always read and follow the label instructions carefully to avoid over-application. Wear protective gloves if necessary, and ensure the environment is well-ventilated if applying sprays. Additionally, monitor your plants closely for any unusual effects after hormone application and adjust usage accordingly.

Can hormonal treatments replace natural plant care methods?
Hormonal treatments should not completely replace natural plant care methods. Instead, they can complement traditional care practices by addressing specific growth challenges. Basic care such as proper watering, lighting, fertilization, and pest management should remain the foundation of plant maintenance, with hormonal treatments serving as supplemental aids when necessary.

Why might some indoor gardeners avoid using growth regulators?
Some indoor gardeners may choose to avoid growth regulators due to concerns over potential negative effects, such as chemical dependency, health risks, or altering the natural balance of plant growth. Others prefer maintaining purely organic practices. These gardeners often focus on natural soil amendments and environmental controls to enhance plant development instead.

Are growth regulators suitable for all indoor plant types?
Not all indoor plants respond similarly to growth regulators, as different species have varied hormonal needs and tolerances. Before applying PGRs, it is essential to understand the specific requirements and characteristics of the plant species you're dealing with. Some plants may benefit substantially, while others might show no apparent effects or may even be adversely affected.

How long does it take to see results from growth regulator applications?
The time frame for observing results after applying growth regulators can vary based on the type of PGR used, the plant species, growth conditions, and the targeted growth phase. Some changes, such as improved growth rates, can be observed within a few weeks, while others, like enhanced flowering or fruiting, may take longer to manifest.

What are the most commonly used plant growth hormones for indoor gardening?
The most commonly used plant growth hormones for indoor gardening include auxins, gibberellins, cytokinins, abscisic acid, and ethylene. Each hormone serves specific functions—from promoting root development and enhancing flowering to regulating stress responses. Understanding how each hormone works can help in selecting the right growth solution for your indoor plants.
