
FAQ About Paul Dirac
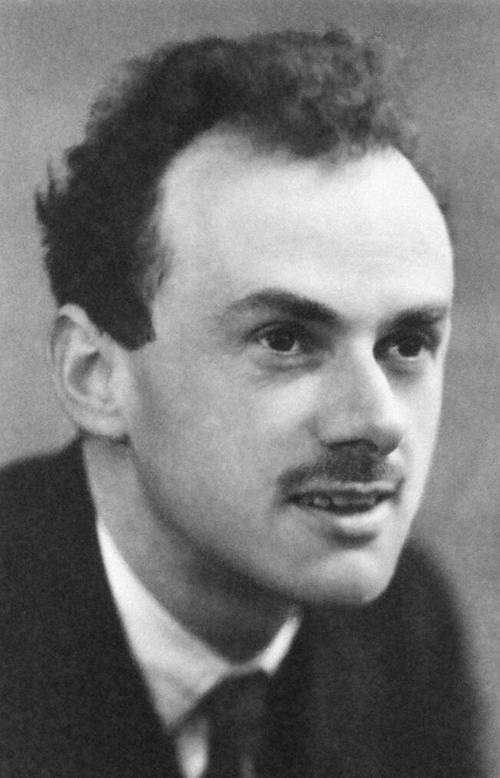
Who was Paul Dirac?
Paul Dirac was a British theoretical physicist renowned for his seminal contributions to quantum mechanics and quantum electrodynamics. He is best known for formulating the Dirac equation, which described the behavior of fermions and predicted the existence of antimatter. Dirac shared the Nobel Prize in Physics in 1933 with Erwin Schrödinger for the discovery of new productive forms of atomic theory.
What is the Dirac equation?
The Dirac equation is a relativistic quantum mechanical wave equation formulated by Paul Dirac in 1928. It provides a description of elementary spin-½ particles, such as electrons, and incorporates both their wave-like properties and the effects of special relativity. Importantly, it predicted the existence of antiparticles, subsequently confirmed with the discovery of the positron.
What contributions did Paul Dirac make to quantum mechanics?
Paul Dirac made several groundbreaking contributions to quantum mechanics. He developed the Dirac equation, which merged quantum mechanics with special relativity and predicted antimatter. He also contributed to the development of quantum field theory and introduced important concepts such as the Dirac delta function and the principles of quantum superposition and quantum statistics.
What is the significance of Dirac's prediction of antimatter?
Dirac's prediction of antimatter was a pivotal moment in physics, suggesting that for every particle, there exists a corresponding antiparticle with opposite charge. This prediction was experimentally validated with the discovery of the positron in 1932, confirming that the universe is governed by symmetry and opening new fields of study in particle physics and cosmology.
How did Paul Dirac influence modern physics?
Paul Dirac's work laid the foundation for many areas of modern physics, particularly in particle physics, quantum field theory, and quantum mechanics. His introduction of the concept of antiparticles and his mathematical formalism have been integral in the development of theoretical and high-energy physics. Dirac's ideas continue to influence both theoretical exploration and practical applications in modern science.
What was Paul Dirac's approach to theoretical physics?
Paul Dirac's approach to theoretical physics was characterized by his emphasis on mathematical beauty and simplicity. He believed that the fundamental laws of nature should be expressed through elegant and simple equations. His pursuit of mathematical harmony often led him to groundbreaking discoveries, such as the Dirac equation, which elegantly combined elements of quantum mechanics and relativity.
What awards did Paul Dirac receive during his career?
Paul Dirac received numerous awards and honors for his contributions to science. Most notably, he was awarded the Nobel Prize in Physics in 1933, which he shared with Erwin Schrödinger. He was also elected a Fellow of the Royal Society, received the Royal Medal, the Copley Medal, and was appointed to the Lucasian Chair of Mathematics at the University of Cambridge, a position once held by Isaac Newton.
Did Paul Dirac work with any other notable scientists?
Throughout his career, Paul Dirac collaborated with several notable scientists. He had a significant correspondence with Niels Bohr, Werner Heisenberg, and Erwin Schrödinger, exchanging ideas on quantum mechanics. Dirac's work was also influenced by the discoveries of Albert Einstein in the realm of relativity, which he integrated into his own theories.
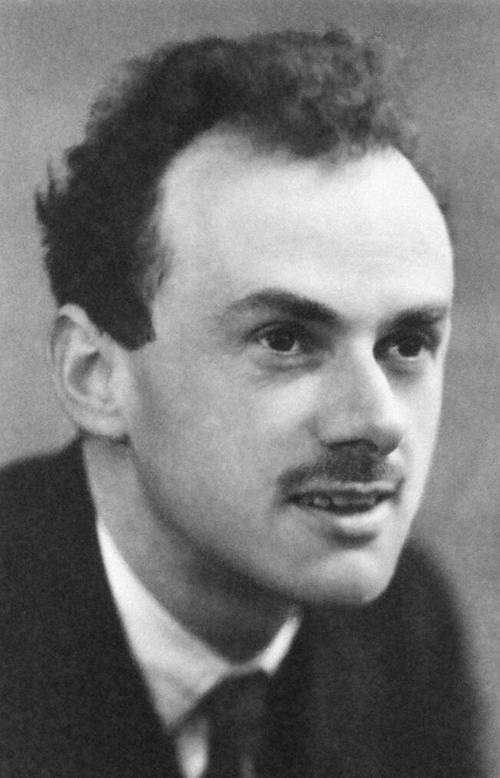
What is the Dirac delta function?
The Dirac delta function, introduced by Paul Dirac, is a mathematical construct used in engineering and physics to model an infinitely small point source or impulse. It is not a function in the traditional sense but a distribution or a generalized function. It is useful in the fields of signal processing, control systems, and quantum mechanics where idealized point-like elements are analyzed.
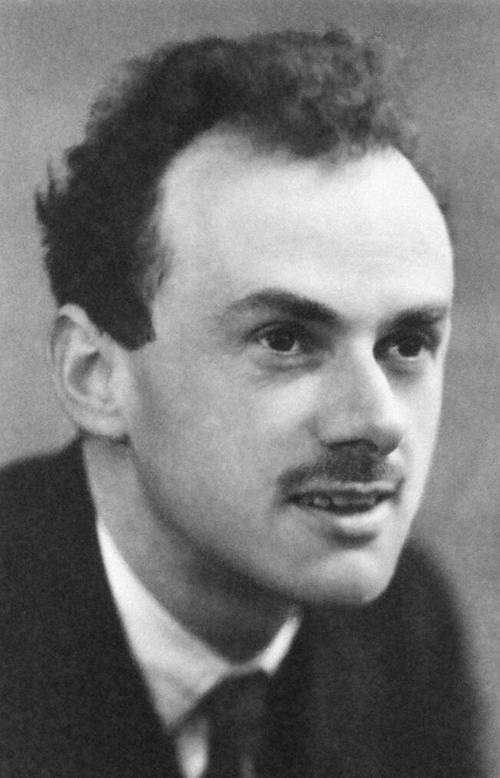
Where did Paul Dirac study and work?
Paul Dirac studied at the University of Bristol, where he obtained degrees in engineering and mathematics. He then moved to the University of Cambridge to pursue a Ph.D. in theoretical physics. After earning his doctorate, Dirac remained at Cambridge, where he eventually became the Lucasian Professor of Mathematics, a prestigious academic position.
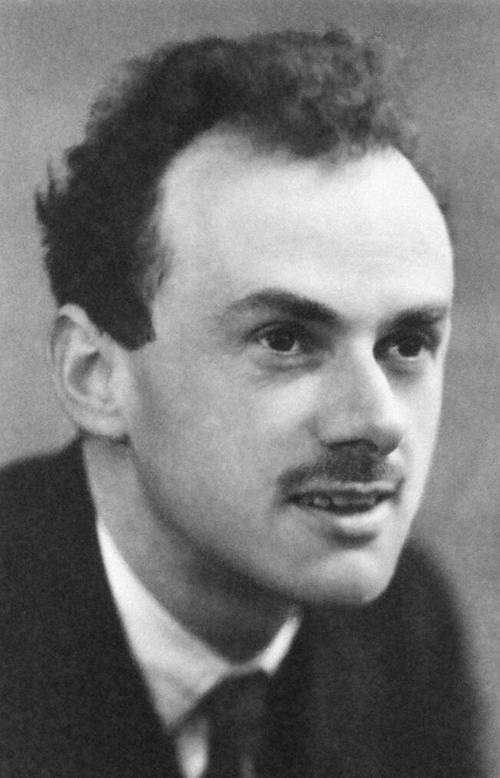
What is quantum field theory, and how did Dirac contribute to it?
Quantum field theory is a fundamental framework in physics that blends quantum mechanics and special relativity to describe the field-based nature of subatomic particles. Paul Dirac's work on the Dirac equation significantly contributed to the development of quantum field theory by explaining the behavior of relativistic electrons and paving the way for concepts like field quantization and particle-antiparticle creation and annihilation.
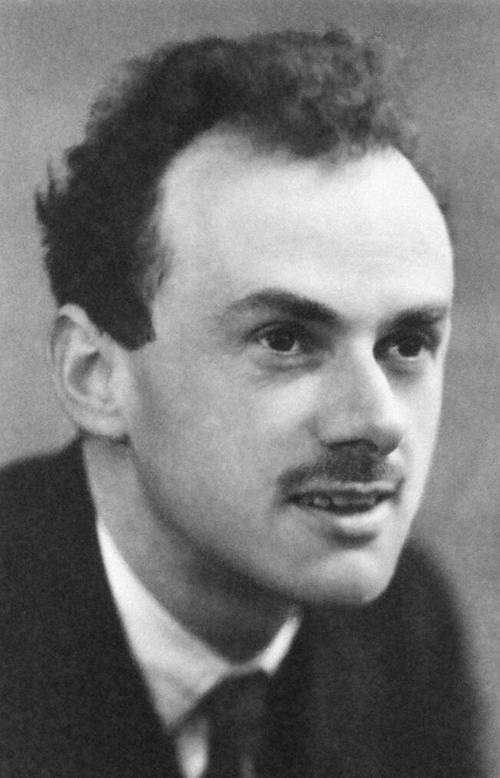
How did Dirac predict the existence of the positron?
Paul Dirac predicted the existence of the positron through his work on the Dirac equation. While solving the equation for electrons, Dirac found negative energy solutions. After careful consideration, he proposed these solutions represented particles with the same mass as electrons but with opposite charge, thus predicting the positron, which was later discovered experimentally by Carl Anderson in 1932.
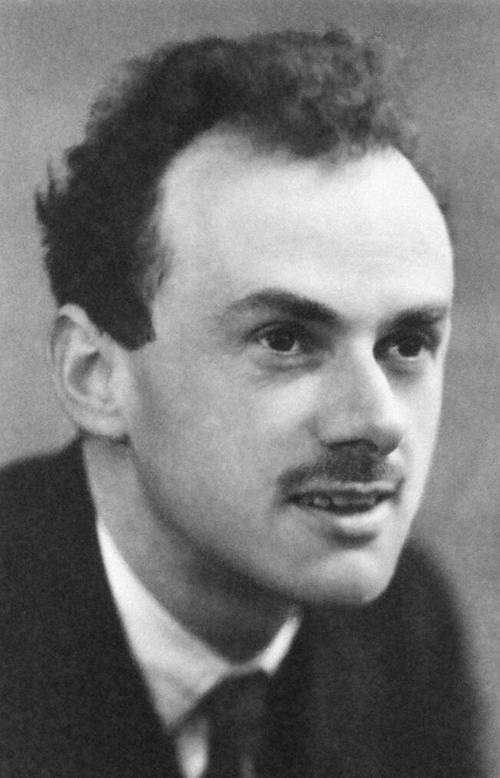
What legacy did Paul Dirac leave in the field of physics?
Paul Dirac's legacy in physics is profound and enduring. He is regarded as one of the principal architects of quantum mechanics. His contributions, such as the Dirac equation and the concept of quantum fields, have shaped the course of theoretical physics. Dirac's insistence on mathematical beauty and precision has continued to guide physicists in the pursuit of understanding the universe.
Did Paul Dirac write any influential books or papers?
Paul Dirac authored several influential books and papers, most notably his textbooks "The Principles of Quantum Mechanics" and "Lectures on Quantum Mechanics," which have become foundational texts in the field. His original papers on the Dirac equation and quantum field theory are also considered classics and continue to be cited for their groundbreaking ideas and clarity.
What was unusual about Dirac's personality and behavior?
Paul Dirac was known for his reserved and somewhat aloof personality. He was intensely focused on his work and preferred solitude to social gatherings. Dirac often spoke very little, earning a reputation for his brevity and directness in conversation. Despite this, he was highly respected and admired for his brilliant insights and dedication to physics.
What other fields besides physics did Dirac influence?
Besides advancing theoretical physics, Dirac's work influenced other scientific disciplines such as mathematics, specifically in areas like linear algebra and calculus through the Dirac delta function and bra-ket notation. His philosophical approach to science also impacted the philosophy of science, especially regarding the roles of symmetry and aesthetics in scientific theories.
How did Paul Dirac's early education influence his career?
Paul Dirac's early education in engineering at the University of Bristol provided him with a strong foundation in mathematics and problem-solving skills, which were crucial in his later work in theoretical physics. His engineering background influenced his precise and methodical approach to scientific research, ultimately guiding his profound contributions to quantum mechanics.
Was Paul Dirac involved in any significant scientific disputes?
Paul Dirac was generally not involved in major scientific disputes, largely due to his preference for theoretical work over public debate. However, his prediction of antiparticles was initially met with skepticism until experimental confirmation. Dirac's work occasionally provoked discussion regarding the interpretation of quantum mechanics, especially concerning his views on symmetry and mathematical beauty.
What institutions did Paul Dirac work with during his lifetime?
Paul Dirac spent much of his academic career at the University of Cambridge, where he was appointed the Lucasian Professor of Mathematics. He later moved to Florida State University, where he continued his research and teaching. Dirac was also a fellow of the Royal Society and received numerous visiting professorships and honorary appointments at institutions around the world.
When and where was Paul Dirac born?
Paul Dirac was born on August 8, 1902, in Bristol, England. He grew up in a family of mixed Swiss and English heritage, which influenced his cultural background. He remained connected to his birthplace throughout his life, even as he traveled extensively for his academic pursuits and collaborations.
