
FAQ About Michael Faraday
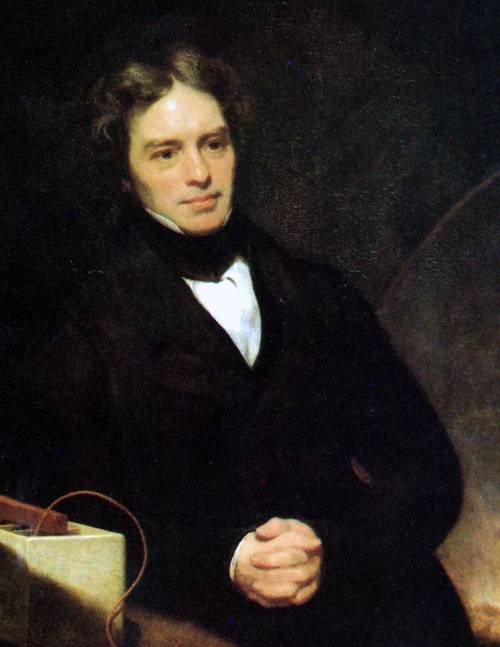
Who was Michael Faraday?
Michael Faraday was a prominent British scientist known for his groundbreaking contributions to electromagnetism and electrochemistry. Born on September 22, 1791, Faraday's work laid the foundation for many technological advancements, particularly in electricity and magnetism. He is credited with inventing the electric motor and discovering electromagnetic induction and laws of electrolysis, influencing future developments in both physics and engineering.
What are Michael Faraday's most significant contributions?
Michael Faraday's most significant contributions include the discovery of electromagnetic induction, which is the process of generating an electric current from a changing magnetic field, the invention of the first electric motor, and laying the groundwork for electromagnetic fields in physics. His laws of electrolysis are also fundamental to the field of electrochemistry. These discoveries have profoundly influenced scientific thought and technological development.
What is electromagnetic induction, and why is it important?
Electromagnetic induction is the process of generating an electric current by changing the magnetic field around a conductor. Discovered by Michael Faraday in 1831, this principle is crucial as it forms the working basis of many electrical devices, including transformers, inductors, and most importantly, electric generators, that convert mechanical energy into electrical energy. This discovery was pivotal in the development of the modern electrical power industry.
How did Michael Faraday impact modern technology?
Michael Faraday's discoveries form the foundation of modern technology. His work on electromagnetic induction allowed for the generation of electricity on a commercial scale, paving the way for modern electricity generation and distribution systems. Faraday’s invention of the electric motor ideated the possibilities of converting electrical into mechanical energy.
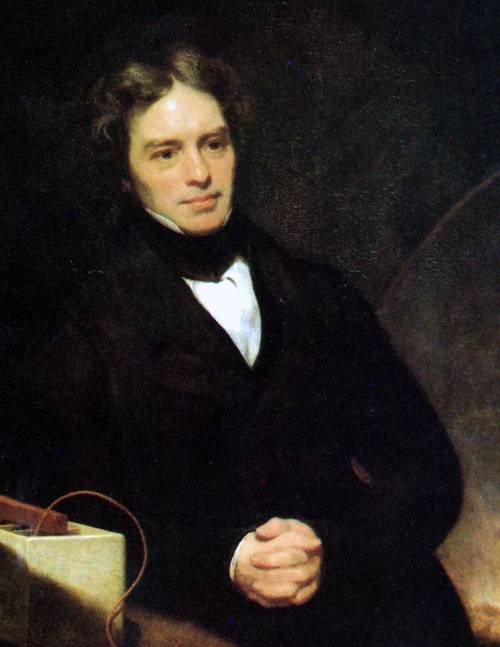
Did Michael Faraday receive any formal education in science?
Unlike many scientists of his caliber, Michael Faraday did not receive much formal education. He was largely self-taught and learned through his work as an assistant to the chemist Humphry Davy at the Royal Institution. Faraday's lack of formal education did not hinder his scientific achievements; rather, it highlights his exceptional ability to learn through observation and experimentation.
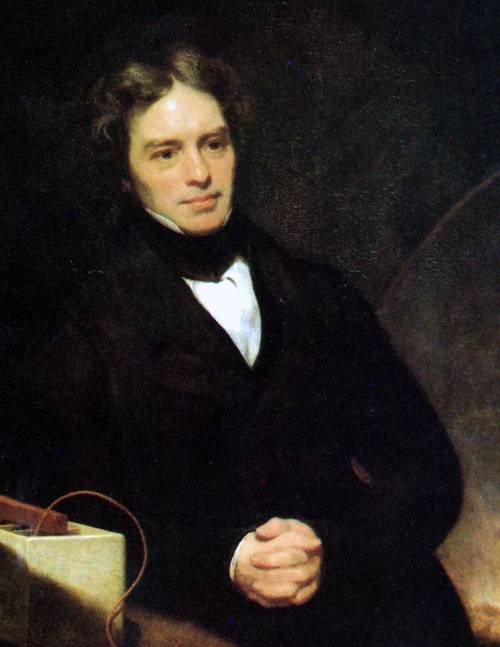
What are Faraday's laws of electrolysis?
Faraday’s laws of electrolysis are quantitative laws that describe the relationships between the amount of substance liberated at an electrode and the quantity of electricity passing through the electrode. The first law states that the mass of substances altered at an electrode during electrolysis is directly proportional to the amount of electricity that passes through the circuit. The second law states that the mass of substances altered by a given quantity of electricity is proportional to their equivalent weight.
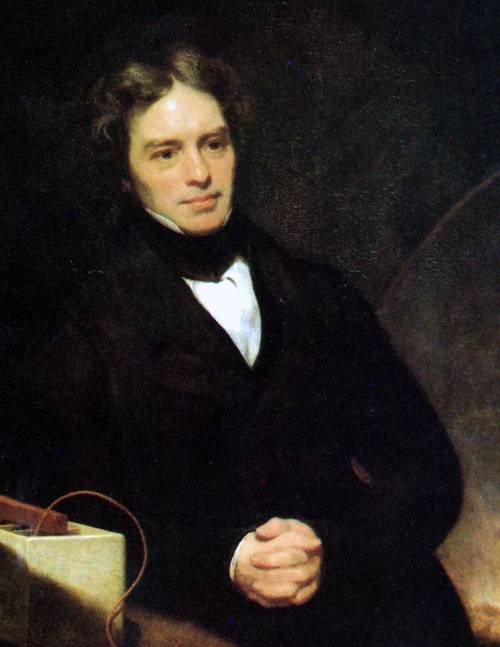
How did Michael Faraday's discoveries influence physics?
Faraday's discoveries laid the groundwork for the electromagnetic field theory, which is fundamental to modern physics. His work on electromagnetic induction led to the development of Maxwell's equations, which describe the behavior of electric and magnetic fields, furthering the understanding of electromagnetism as a unified physical force. These ideas eventually contributed to the development of quantum mechanics and relativity.
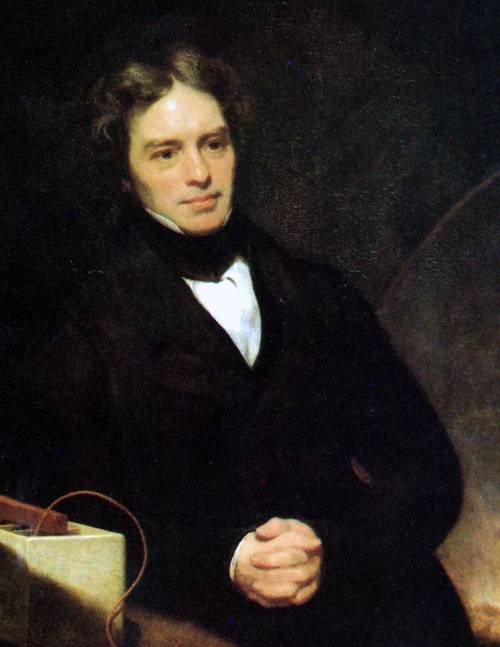
What challenges did Michael Faraday face in his scientific career?
Despite his significant contributions, Faraday faced several challenges. He came from a humble background and struggled with limited formal education. His early work as an assistant meant he had to gain recognition in the scientific community, dominated by social elites. Additionally, Faraday suffered from nervous breakdowns later in life, which limited his scientific activities.
What was Faraday's role at the Royal Institution?
Michael Faraday initially joined the Royal Institution as a laboratory assistant under Humphry Davy. Over time, he rose to become the Director of the Laboratory. His role was crucial in expanding the institution’s research agenda and he conducted numerous experiments and popular lectures at the Institution. Faraday's roles helped transform the Royal Institution into a leading center for scientific research during his time.
Did Michael Faraday have any other scientific interests?
Aside from electromagnetism and electrochemistry, Michael Faraday had interests in chemistry and materials science. He was the discoverer of benzene and investigated the properties of gases. He also conducted studies on the liquefaction of gases, the nature of optical glass, and even contributed to early molecular theories.
What is the Faraday effect?
The Faraday effect is the phenomenon where the polarization of light is rotated when it passes through a material in the presence of a strong magnetic field. Discovered by Michael Faraday in 1845, this was the first experimental evidence of the relationship between light and magnetism, supporting the theories of electromagnetic fields and contributing to the field of magneto-optics.
What is a Faraday cage and how does it work?
A Faraday cage is an enclosure used to block electromagnetic fields. It works by distributing charge or radiation around the cage’s exterior, effectively shielding its contents from external static and non-static electric fields. Named after Michael Faraday, who built the first such cage in 1836, it is commonly used in scientific experiments and in protecting electronic equipment from interference.
How did Faraday's religious beliefs influence his work?
Michael Faraday was a devout member of the Sandemanian Church, and his religious beliefs strongly influenced his approach to science. Faraday saw his work as a way to honor God by understanding His creation. Though his religious views at times separated him from more conventional scientific circles, they also gave him a distinct perspective regarding the interconnectedness of natural phenomena.
Where and when was Michael Faraday born?
Michael Faraday was born on September 22, 1791, in Newington Butts, which is now part of the London Borough of Southwark, England. He grew up in a poor family and received only basic formal education before beginning his career as an apprentice to a local bookbinder.
What was Michael Faraday's influence on later scientists?
Faraday's work profoundly influenced later scientists, notably James Clerk Maxwell, who mathematically refined Faraday’s theories in the form of Maxwell's equations, crucial for electromagnetic theory. Albert Einstein also regarded Faraday highly, citing his work in developing the theory of relativity. Faraday's experimental and intuitive approach remain inspirational to physicists and chemists alike.
What were some personal qualities of Michael Faraday noted by others?
Michael Faraday was noted for his humility, persistence, and passion for science. Despite his substantial scientific contributions, he remained modest and keenly aware of his limitations. His dedication and ability to communicate complex scientific ideas clearly made him an effective lecturer and beloved figure among his peers and the public.
Is there any notable institution named after Michael Faraday?
Yes, several institutions and awards are named after Michael Faraday, reflecting his impact on science. Notably, The Faraday Institute for Science and Religion and the annual Faraday Medal awarded by the Institute of Physics bear his name. These reflect his lasting legacy within the scientific community and beyond.
How did Michael Faraday approach teaching and public lectures?
Michael Faraday was renowned for his public lectures, particularly at the Royal Institution, where he simplified complex scientific ideas into language accessible to lay audiences. He pioneered the popular Christmas Lectures for young people, emphasizing hands-on experiments to illustrate scientific principles, inspiring countless future scientists.
What was the impact of Faraday's electric motor invention?
The invention of the electric motor by Michael Faraday revolutionized the understanding of the relationship between electricity and magnetism, offering practical applications that continue to underpin modern machinery and technology. His motor demonstrated the principle of electromagnetic rotation, critical to developing electric generators and vehicles.
How does Faraday's work relate to modern electrical engineering?
Faraday's discoveries and experimental techniques significantly influenced the field of electrical engineering. The principles of electromagnetic induction lie at the heart of modern power generation and electrical transformer technologies. His work also underpins communications technology, with the electromagnetic theory crucial to understanding radio, television, and data transmission systems.
